Transport Layer
Transport-layer services
- Provide logical communication between application processes running on different hosts
- For sender, it breaks application messages into segments, then passes to network layer (receiver reassembles the segments)
TCP
- Reliable, in-order
- congestion control
- flow control
- connection setup
UDP - Best effort delivery
Multiplexing and demultiplexing
Multiplexing - handle data from multiple sockets, add transport header
Demultiplexing - User header info to deliver received segment to correct socket
- Host receives IP datagrams, containing IP and port number for both source and destinations
- Host use IP address and port number to direct segment to appropriate sockets
- Connectionless demultiplexing (UDP)
- Datagram must contain dest IP and port # (only use destination IP and port number)
- Datagrams with same dest port # would be send to same dest socket
- One socket with multiple client at the same time
- Connection oriented demultiplexing (TCP)
- Must have IP and port number from both source and destination
- Received use all 4 values to direct segment to appropriate socket
- System may support multiple TCP socket simultaneously
- All client uses the same server port (different socket), since the server port alone does not distinguish connections
Hackers can scan port to find vulnerabilities
Connectionless transport: UDP
- No handshaking
- Each UDP packet is independent from others
- May be lost or delivered out of order
Advantages:
- No RTT delay for establishing connections
- Simple, no connection required between client and server side
- Smaller header size
- No congestion control
- Can blast away as fast as desired
Use Cases:
- Streaming multimedia apps (loss tolerant, rate sensitive)
- DNS
- SNMP
- HTTP/3
HTTP/3 added congestion control and needed reliability at application layer, to improve reliability for UDP
! 200
Checksums
- detect errors (flipped bits) in transmitted segment
- Sender compute and add the checksum into UDP, receive computes and check if the checksum matches.
- weak protection
- Can either drop the currently packet or report error
Principles of reliable data transfer
- rdt 1.0
- assume no bit error and loss of packet
- rdt 2.0
- with error, send ACK and NAK to acknowledge presence of error
- ACK may be corrupted -> duplicate
- Hence need to add sequence number to each packet
- Can remove NAK, by sending ACK with previous sequence number
- rdt 3.0 - with error and loss
- Add a timeout and countdown to interrupt after amount of time
Pipelining
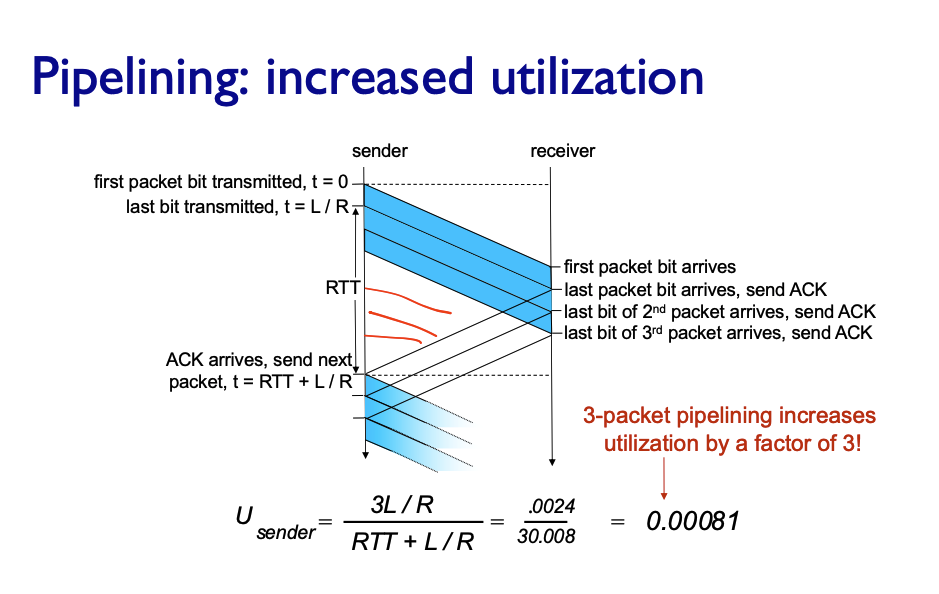
Go-Back-N (GBN)
- Sender has window up to N, consecutively transmitted
- timer for oldest in-flight packet
- Always send ACK for correctly-received packet so far
- can discard or buffer (depend on implementation)
- ! 300
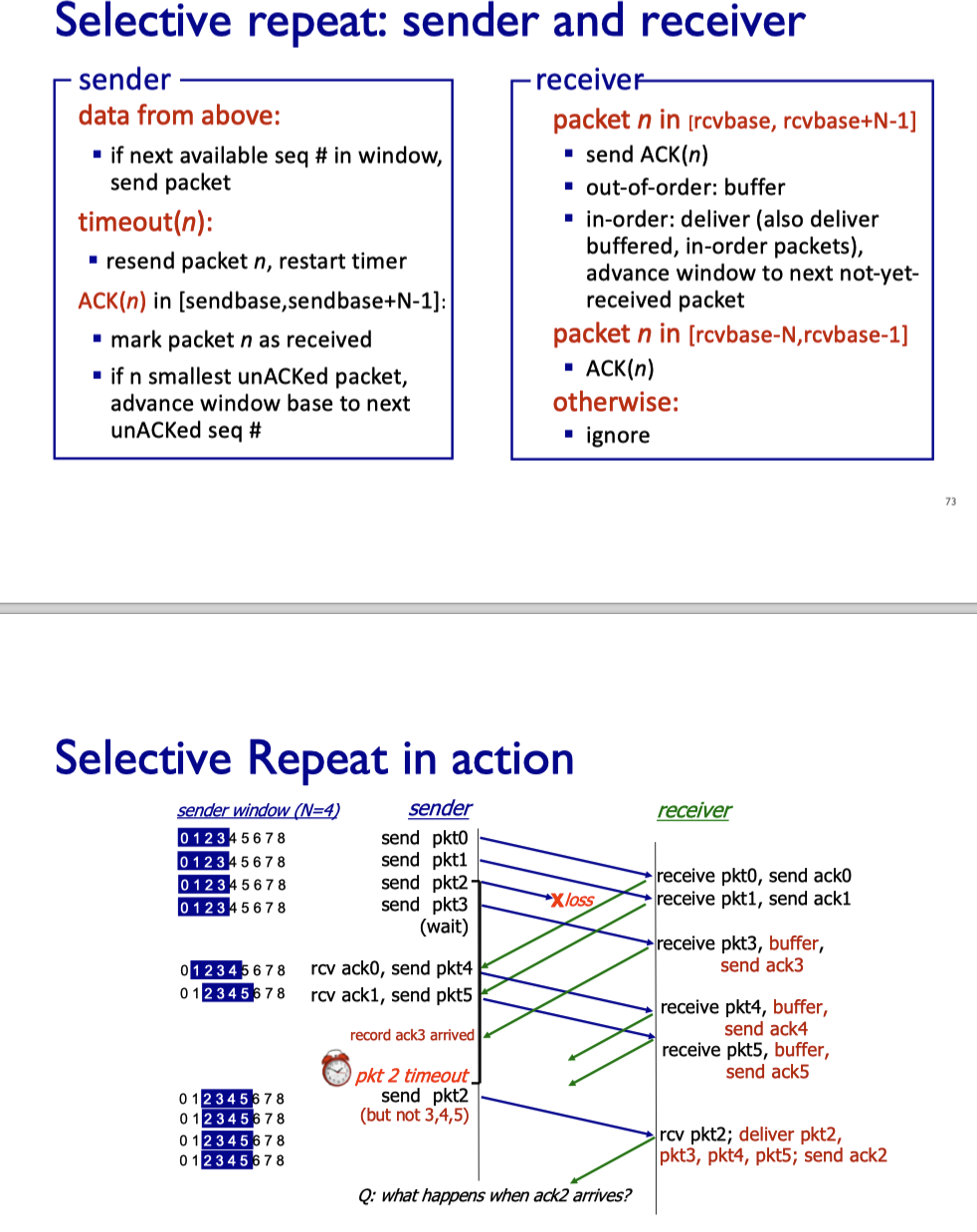
Selective repeat
- Receiver individually acknowledges all correctly received packets
- buffers packets as needed
- When timeout, retransmits individually for unACKed packets
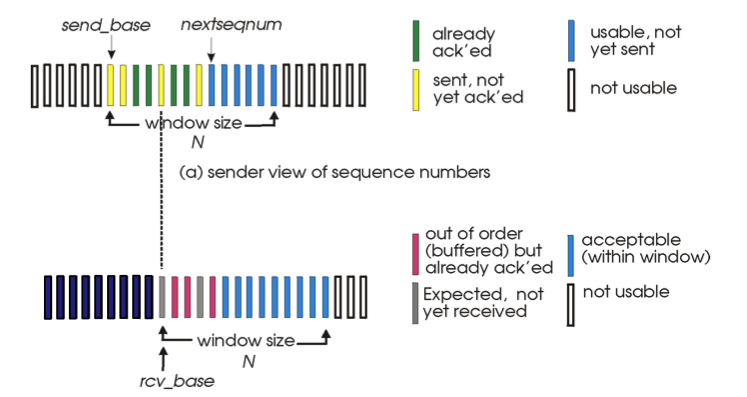
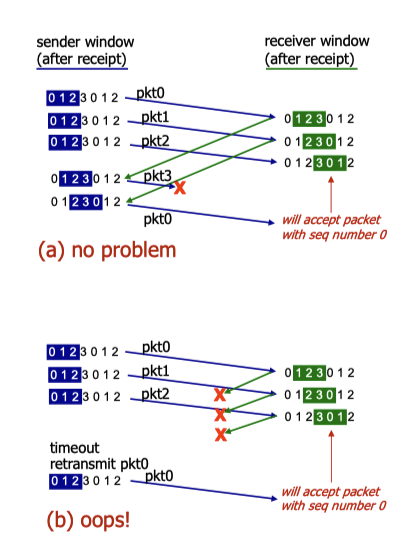
- Sender window size <= 1/2 of sequence number space
- avoid ACK old packets as new packets
Connection-oriented transport: TCP
- TCP properties
- Point to point (one sender and one receiver)
- reliable, in-order byte
- no "message boundaries", not distinct and self-contained messages
- full duplex data (bi-directional data flow in the same connection)
- cumulative ACKs
- pipelining
- connection-oriented
- handshaking to initialise sender and receiver before data exchanges
- flow control
- send will not overwhelm receiver
Segment structure
! 300
Reliable data transfer
- TCP header is minimal 20 bytes
- MSS - maximums segment size
- MTU - maximum transmission unit
- !100
- Sequence number
- ACK seq number = next expected byte = seqno + length (data)
- ISN and randomised, avoid the scenario of miss understanding the new packet as old missing packet

- Server can send Response and ACK in the same packet rather than two parallel ones
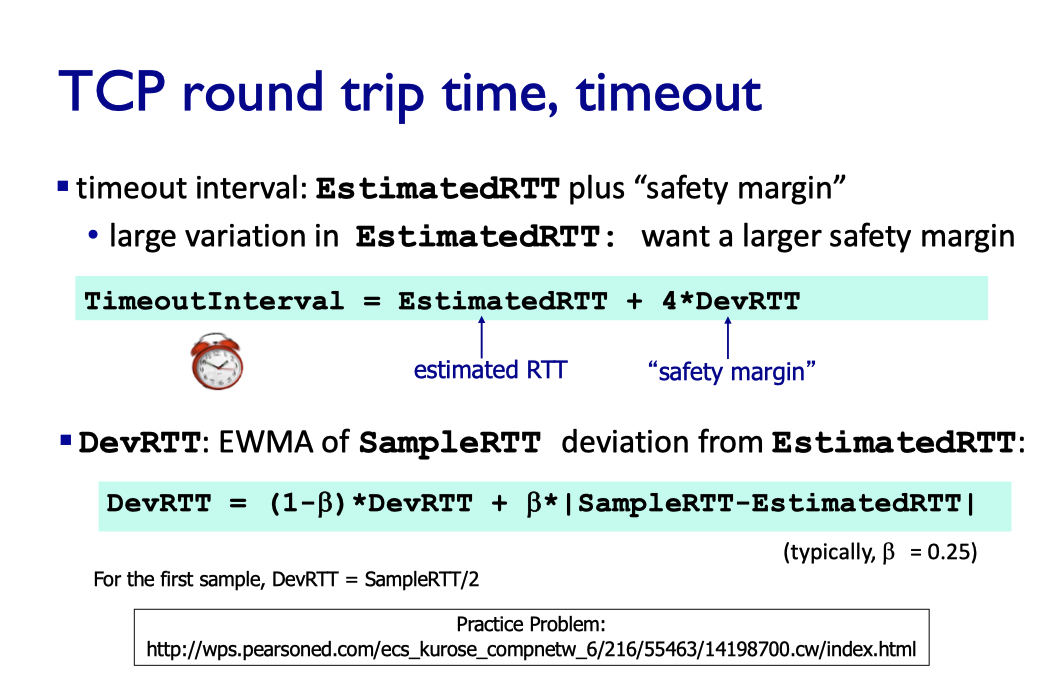
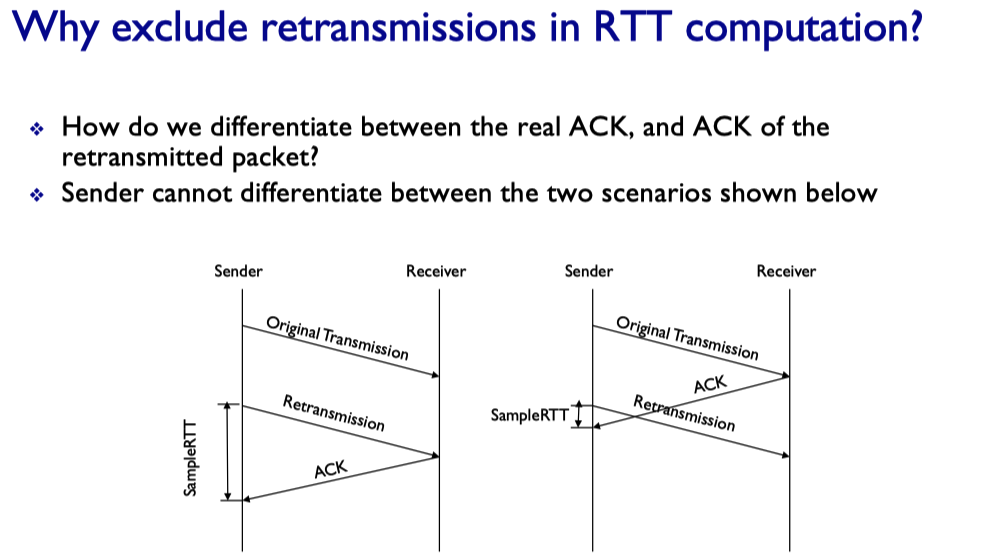
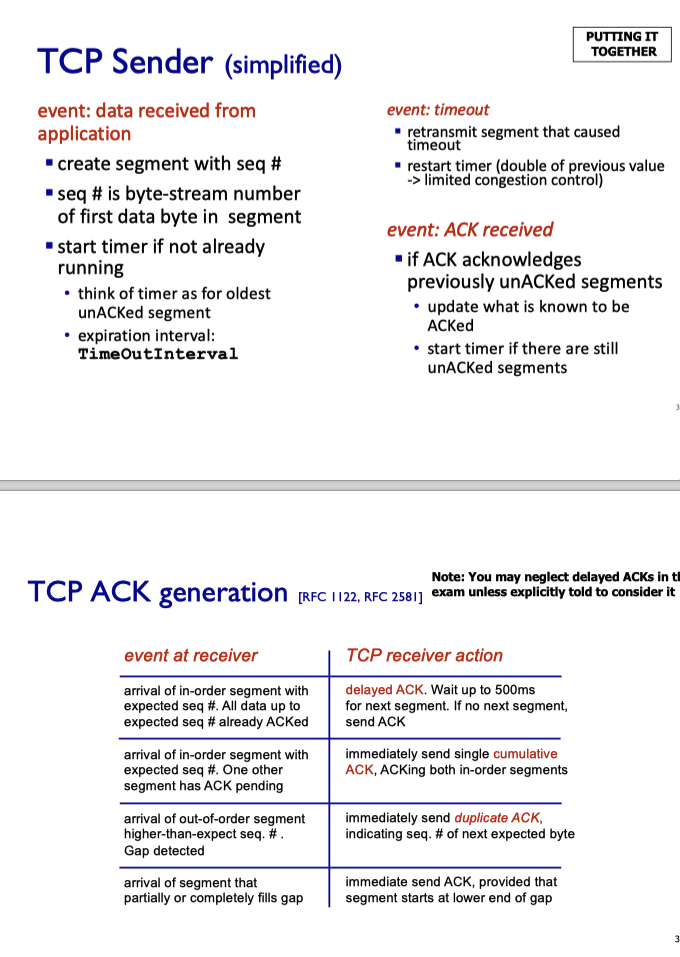
TCP round trip time, timeout
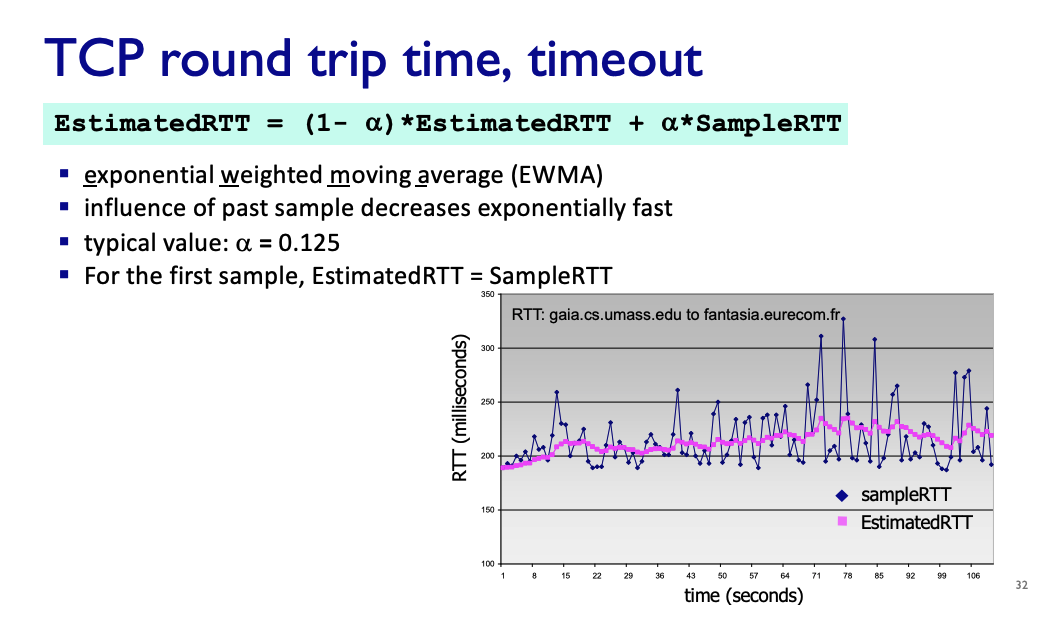
- Estimate RTT
- Sample RTT: time from segment transmission until ACK received
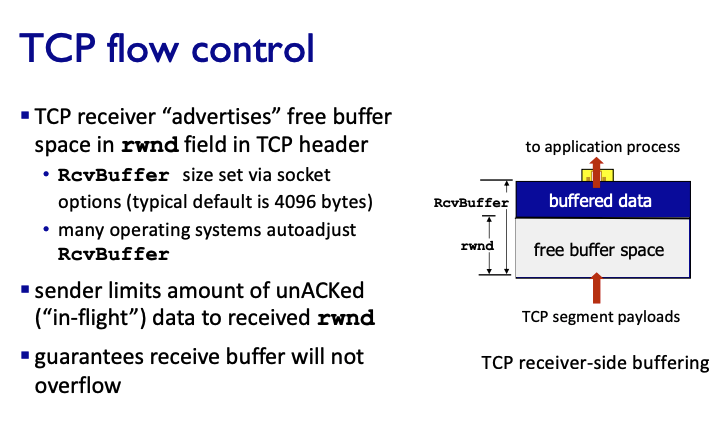
TCP flow control
- receiver controls sender, so sender won't overflow receiver's buffer by transmitting too much, too fast
Connection management
- The timeout for the SYN packet is usually 75 seconds
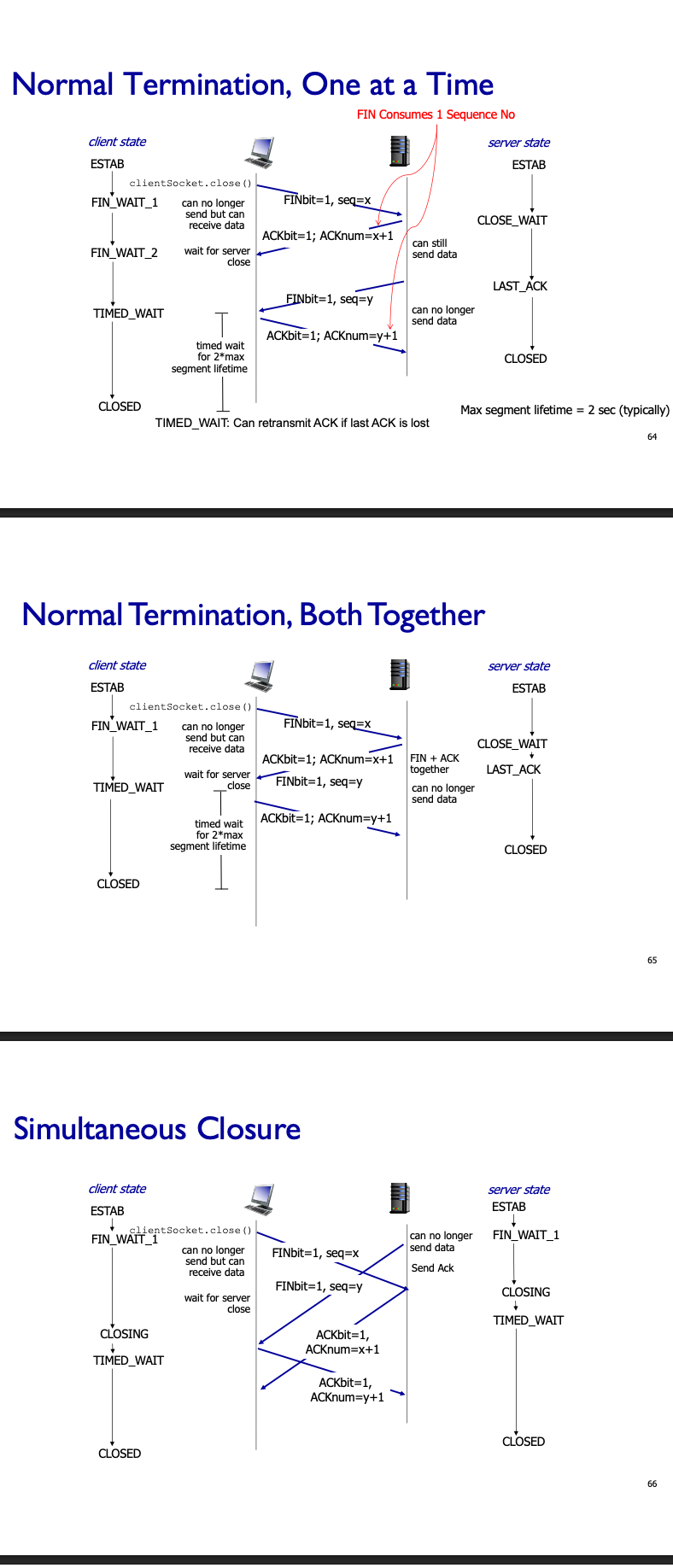
Closing a connection
- Client, server each close their side of connection
- send TCP segment with FIN bit = 1
- respond to received FIN with ACK
- on receiving FIN, ACK can be combined with own FIN
- simultaneous FIN exchanges can be handled
Principles of congestion control
-
cause lost packets and long delays
-
end-end congestion control
- no feedback from network
- inferred from end-system observe loss and delay
- TCP's approach
-
network assisted congestion control
- router provide feedback to system
- explicit rate for sender to send at
TCP congestion control
- Congestion window
- how many bytes can be sent without overflowing routers
- in units of MSS (maximum segment size)
- Flow control window
- how many bytes can be sent without overflowing receiver's buffer
- TCP sending rate =
cwnd/ RTT (bytes/sec)
Detecting congestion
- duplicate ACKs
- indicate network capable of delivering some segments
- timeout
- more serious, since the server don't even have resource to response a small ACK
- several losses already
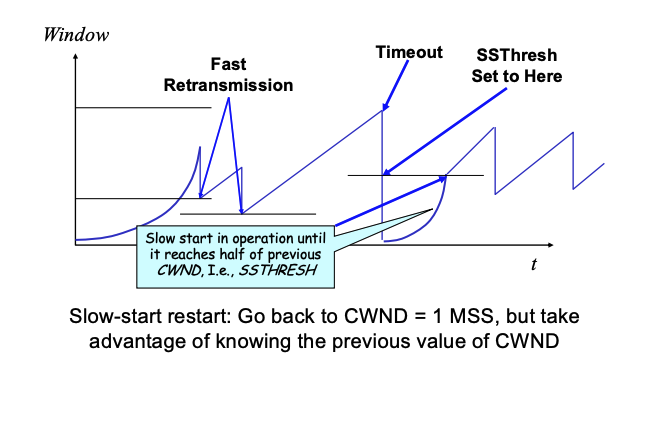
TCP slow start (bandwidth discovery)
- when connection begins, increase rate exponentially until first loss event
- exponential growth
Additive increase multiplicative decrease (AIMD)
- Congestion avoidance - oscillate around its value, probing (rate increase) and back-off (rate decrease)
- additive increase - increase
cwndby 1 MSS every RTT until loss detected - multiplicative decrease - cut
cwndin half after loss
Slow start threshold (ssthreash)
- convert to CA when
cwnd = ssthresh, sender switches from slow-start to AIMD style increase- on loss,
ssthresh = cwnd / 2
- on loss,
cwnd = MIN_INT
ssthresh = MAX_INT
if cwnd < ssthresh:
cwnd += 1
else:
cwnd = cwnd + 1 / cwnd (after one RTT, cwnd += 1)
dupACKcount++
if dupACKcount = 3:
ssthresh = cwnd / 2
cwnd = cwnd / 2
On timeout:
ssthresh = cwnd / 2
cwnd = 1
TCP flavours
- TCP Tahoe
cwnd = 1on triple dup ACK and timeout
- TCP Reno
cwnd = 1on timeoutcwnd = cwnd / 2on triple dup ACK