Java Interview Questions
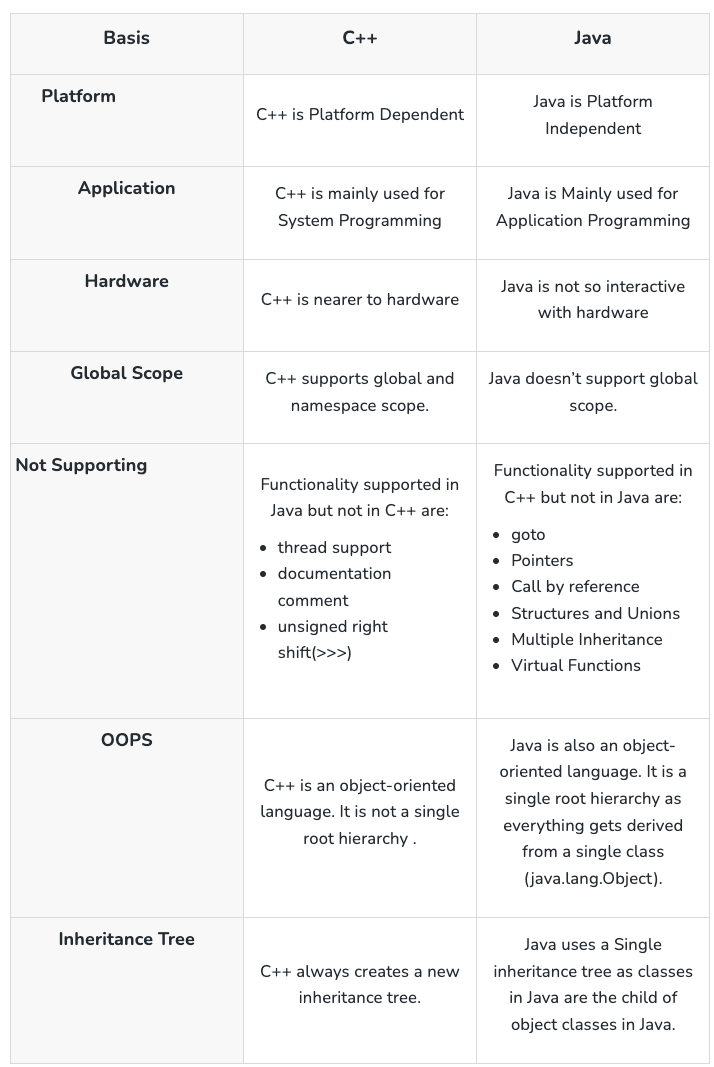
Java vs C++
Java vs Python
Similarities:
- High-Level Languages:
• Both Java and Python are high-level programming languages, meaning they are easier to read and write compared to low-level languages. - Object-Oriented:
• Both support object-oriented programming (OOP) principles such as classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism. - Large Standard Libraries:
• Both languages come with extensive standard libraries that provide many built-in functions and modules for various tasks, reducing the need to write code from scratch. - Cross-Platform:
Programs written in Java and Python can run on various operating systems without modification, as long as the respective runtime environments (JVM for Java and Python interpreter for Python) are available.
Differences:
- Syntax:
• Python: Known for its simple and readable syntax, Python uses indentation to define code blocks.
• Java: Uses more verbose syntax with curly braces to define code blocks and semicolons to terminate statements. - Typing System:
• Python: Dynamically typed, meaning variable types are determined at runtime, which can lead to more flexible but potentially error-prone code.
• Java: Statically typed, meaning variable types are declared explicitly and checked at compile-time, leading to potentially more robust but less flexible code. - Execution:
• Python: Interpreted language, code is executed line by line, which can result in slower execution times.
• Java: Compiled to bytecode, which is then executed by the JVM, often resulting in faster execution compared to Python. - Performance:
• Python: Generally slower due to its interpreted nature and dynamic typing.
• Java: Typically faster because of its compiled bytecode and static typing. - Use Cases:
• Python: Preferred for scripting, automation, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and rapid application development.
• Java: Widely used for building large-scale enterprise applications, Android app development, and applications requiring high performance.
- Concurrency:
• Python: Uses the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) which can be a bottleneck for multi-threaded programs.
• Java: Provides robust multi-threading support and concurrency through its built-in libraries and the JVM.
- Memory Management:
• Python: Uses automatic memory management with garbage collection, but developers have less control over memory allocation.
• Java: Also uses automatic garbage collection, but with more advanced tuning options and greater control over memory management.
- Community and Ecosystem:
• Python: Strong in scientific computing, data science, machine learning, and web development with frameworks like Django and Flask.
• Java: Strong in enterprise environments, large-scale web applications, and mobile development with frameworks like Spring and Hibernate, and Android development.
- Development Speed:
• Python: Typically faster development due to simpler syntax and dynamic typing, making it ideal for rapid prototyping.
• Java: May have a steeper learning curve and slower development time due to verbose syntax and static typing.
- Compilation and Interpretation:
• Python: Interpreted language, meaning source code is executed directly by the Python interpreter.
• Java: Compiled to bytecode, which is then interpreted or compiled to machine code by the JVM.