DNS
Domain Name System
- Convert human readable name to IP address
- like a phone book
- two way handshake
- Provided by service like CloudFare
- IP address usually caching on the computer
- firewall will block request if indicated
- TLD, Top Level Domain (.com)
Disadvantages of DNS
- Access to DNS server may introduce a slight delay, but can be cached locally
- Complex to manage, and usually managed by governments, ISPs and companies
- CDN resolver - initiate query sequence and forward to other DNS name servers
- Root-level name servers - Maintain name of server based on TLD
- Top-level domain (TLD) name servers: These servers hold the IP addresses of authoritative name servers. The querying party will get a list of IP addresses that belong to the authoritative servers of the organisation.
- Authoritative name servers: These are the organization’s DNS name servers that provide the IP addresses of the web or application servers.
Caching
- implemented in the browser to store DNS
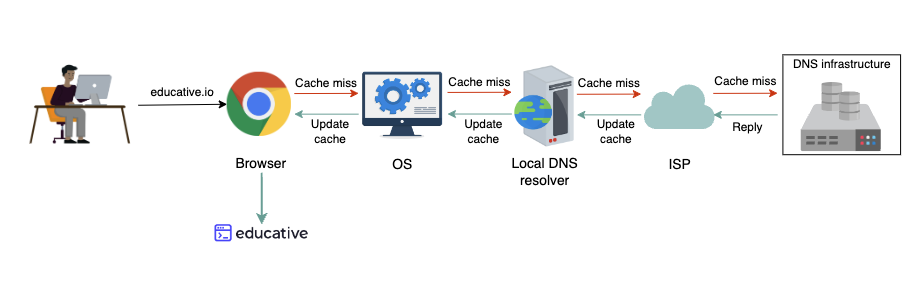
DNS as distributed system
- avoid being single point of failure
- low query latency
- highly available across the globe
- highly reliable
- caching
- server replication
- UDP protocol