Communication
HTTP
- method of encoding and transfer data between the client and server
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
-
Contains the information of the order for packages of information sent through IP
-
All packets sent are guaranteed to reach the destination in the original order and without corruption
- Request missing packets, and resend from the server (retransmission of lost package)
-
3 way hand shake, client send synchronisation message, server replies with acknowledgement and another synchronisation, then client sends the final acknowledgement
-
TCP is useful for applications that require high reliability but are less time critical.
- TCP has higher latency
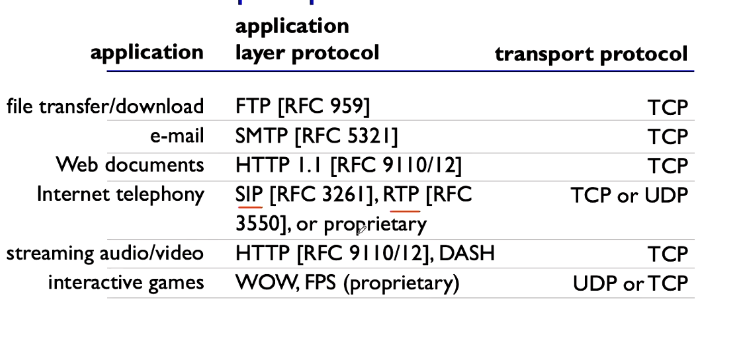
- SMTP - for emails
- SSH - for virtue machines
- WS - web socket
-
Reliable transport
-
Flow control - won't overwhelm the receiver
-
Congestion control - throttle sender when the network is overloaded
-
No guarantee on timing, minimum throughput, security
-
Requires setup - three way hand shake
UDP - User Datagram Protocol
-
no hand shack required
-
order and retransmission are not guarantee
-
must faster
-
VoIP, video chat, streaming, and realtime multiplayer games.
-
The rate for sending (not receiving) the packet are guaranteed
Use UDP over TCP when:
- You need the lowest latency
- Late data is worse than loss of data
- You want to implement your own error correction