Cache
Types of cache
- Caches can be located on the client side (OS or browser), server side, or in a distinct cache layer.
- CDNs are considered a type of cache.
- Reverse proxies and caches such as Varnish can serve static and dynamic content directly. Web servers can also cache requests, returning responses without having to contact application servers.
- Your database usually includes some level of caching in a default configuration, optimized for a generic use case. Tweaking these settings for specific usage patterns can further boost performance.
Application caching
In-memory caches such as Memcached and Redis are key-value stores between your application and your data storage. Since the data is held in RAM, it is much faster than typical databases where data is stored on disk. RAM is more limited than disk, so cache invalidation algorithms such as least recently used (LRU) can help invalidate 'cold' entries and keep 'hot' data in RAM.
High performance
- We used consistent hashing. Finding a key under this algorithm requires a time complexity of O(log(N)), where N represents the number of cache shards.
- Inside a cache server, keys are located using hash tables that require constant time on average.
- The LRU eviction approach uses a constant time to access and update cache entries in a doubly linked list.
- The communication between cache clients and servers is done through TCP and UDP protocols, which is also very fast.
- Since we added more replicas, these can reduce the performance penalties that we have to face if there’s a high request load on a single machine.
- An important feature of the design is adding, retrieving, and serving data from the RAM. Therefore, the latency to perform these operations is quite low.
Redis
Redis has the following additional features:
- Persistence option
- Built-in data structures such as sorted sets and lists
There are multiple levels you can cache that fall into two general categories: database queries and objects:
- Row level
- Query-level
- Fully-formed serialisable objects
- Fully-rendered HTML
Generally, you should try to avoid file-based caching, as it makes cloning and auto-scaling more difficult.
When to update cache
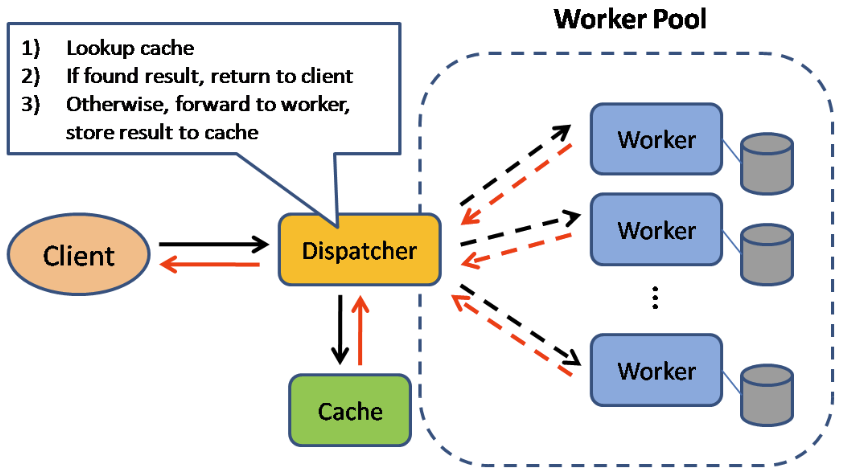
Cache-aside (Memcached)
- Process
- Look for entry in cache, resulting in a cache miss
- Load entry from the database
- Add entry to cache
- Return entry
- Only requested data is cached, which avoids filling up the cache with data that isn't requested.
Disadvantages
- Each cache miss results in three trips, which can cause a noticeable delay.
- Data can become stale if it is updated in the database.
- Can be mitigated by setting a TTL on cache
Write through
- Process
- Application adds/updates entry in cache
- Cache synchronously writes entry to data store
- Return
- Date in the cache is not stale
- User should be more tolerant to latency when write data
Disadvantages
- Slower due to the write
- Most data written might never be read, which can be minimised with a TTL.
Write behind (write-back)
- Process
- Add/update entry in cache
- Asynchronously write entry to the data store, improving write performance
Disadvantage(s): write-behind
- There could be data loss if the cache goes down prior to its contents hitting the data store.
- It is more complex to implement write-behind than it is to implement cache-aside or write-through.
Refresh-ahead
- You can configure the cache to automatically refresh any recently accessed cache entry prior to its expiration.
- Not accurately predicting which items are likely to be needed in the future can result in reduced performance than without refresh-ahead.
Cache Disadvantages
- Need to maintain consistency between caches and the source of truth such as the database through cache invalidation.
- Cache invalidation is a difficult problem, there is additional complexity associated with when to update the cache.
- Need to make application changes such as adding Redis or memcached.
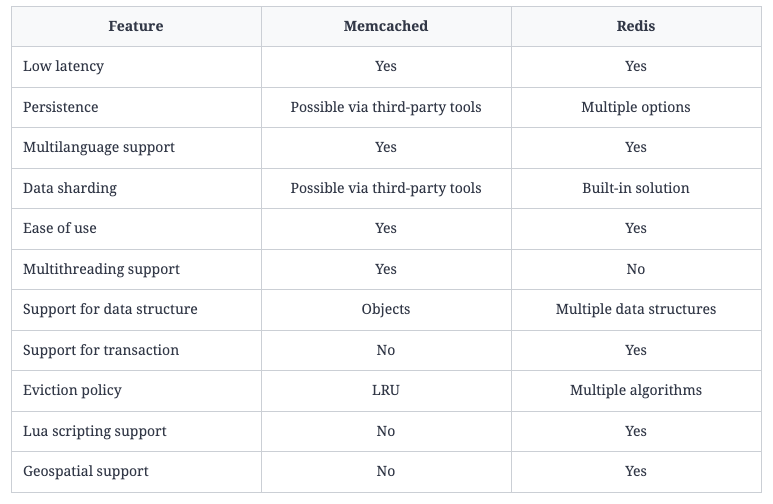
Memcached vs Redis
- Memcached is preferred for smaller, simpler read-heavy systems, whereas Redis is useful for systems that are complex and are both read- and write-heavy.
- Simplicity - Memcached need manual managing of the clusters, where as redis automate most of the data division tasks
- Persistence - Redis is persistent
- Data types - Memcached only supported object, redis support strings, hash maps, sorted set ...